Understanding SD-WAN vs VPN: Which is Better for You?
In today’s digital landscape, deciding between SD-WAN and VPN can be crucial for optimizing your network for your home or business and/or employees. SD-WAN (Software-Defined Wide Area Network) and VPN (Virtual Private Network) serve different networking needs, offering unique features, benefits, and applications. While SD-WAN is tailored for managing WANs with software-defined methods to boost traffic routing efficiency across large distances, VPNs primarily ensure a secure tunnel for data transmission to protect privacy. This distinction makes understanding sd-wan vs vpn vital for anyone looking to enhance their network architecture, be it for home or business needs.
Both technologies cater to the demand for secure and efficient networking, with SD-WAN providing an edge in centralized control, flexibility, and performance adaptation across varied traffic types and conditions. On the other hand, VPNs focus on data confidentiality through encryption, although they usually depend on a single link for data transmission. For businesses and home users finding the right IT company to set up VPNs or SD-WAN is essential, as SD-WAN’s advanced features like dynamic path selection and integrated security tools can significantly reduce latency and bolster the overall security posture.
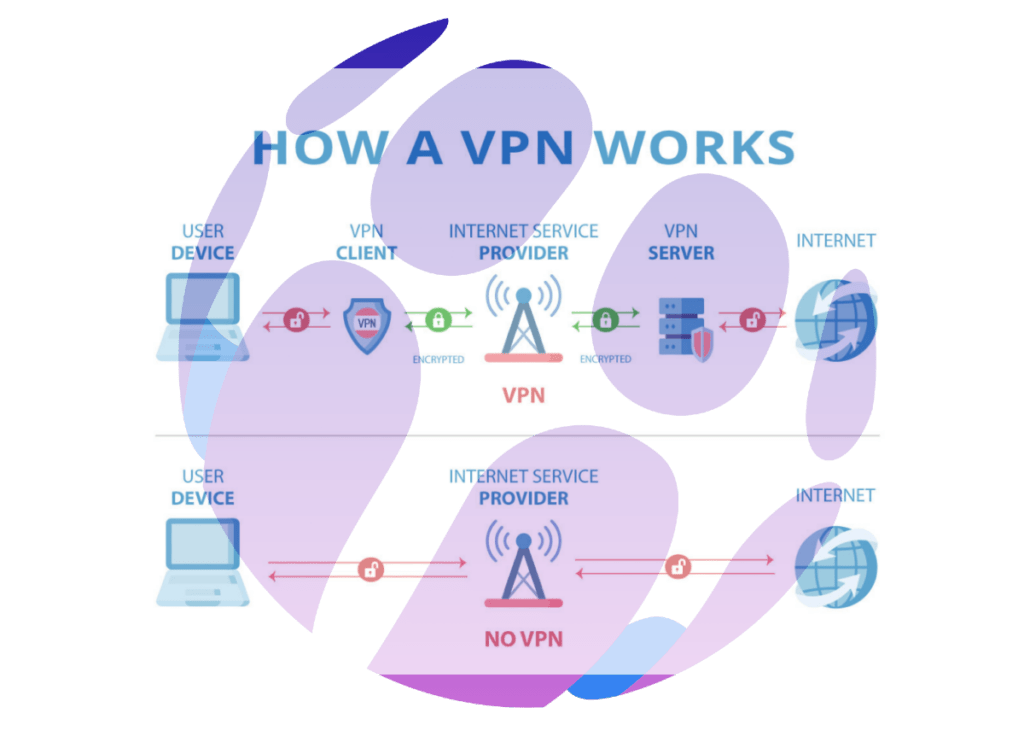
Understanding VPNs
Key Features and Functions of VPNs
- Security and Privacy: VPNs are designed to enhance online security and privacy by encrypting data and routing internet traffic through secure servers. This encryption helps protect against cyber threats like identity theft and data breaches. VPNs also mask users’ IP addresses, providing anonymity and protecting personal information from being exposed online.
- Access and Freedom: By routing traffic through servers in different locations, VPNs allow users to bypass geo-restrictions and access content from around the world. This is particularly useful for accessing streaming services, websites, and applications that are restricted in certain countries. Additionally, VPNs help avoid price discrimination by hiding users’ locations.
- Performance Factors: While VPNs generally provide a stable and secure connection, their performance can be affected by factors such as geographic distance, traffic surges, and reliance on public internet infrastructure. These factors can lead to latency issues and slower data transmission speeds, especially when the VPN server is far from the user’s actual location.
Comparative Cost Analysis
- Pricing Models: VPN services are available in both free and paid versions. Paid VPNs typically offer more reliable connections, better speeds, and advanced security features compared to free versions. The cost of VPN services can vary, with some providers offering plans starting at approximately $7 per user per month.
- Cost-Effectiveness: In comparison to SD-WAN, VPNs are generally more affordable and are a cost-effective solution for individuals and small businesses that require basic encryption and security for their internet connections. However, for larger enterprises with more complex networking needs, SD-WAN might be a more suitable option due to its comprehensive network management capabilities.
VPN Protocols and Encryption
- Protocols Used: VPNs utilize various protocols to secure and transport data across the internet. Common protocols include PPTP, L2TP, SSTP, IKEv2, and OpenVPN. Each protocol has its strengths and is chosen based on the security level required and the device compatibility.
- Encryption Standards: VPNs employ strong encryption standards to secure data transmissions. This encryption ensures that even if data is intercepted, it cannot be read without the proper decryption key. This is crucial for protecting sensitive information during online transactions, particularly on public Wi-Fi networks.
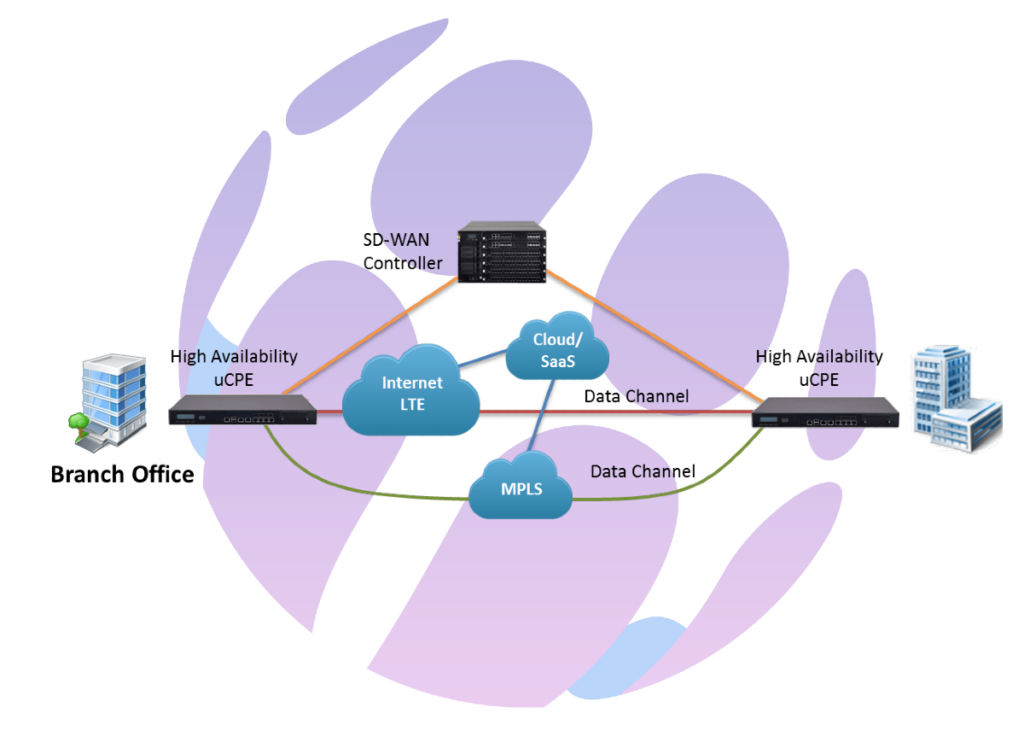
Understanding SD-WAN
SD-WAN (Software-Defined Wide Area Network) revolutionizes the management and optimization of wide area networks by leveraging software-defined technologies for enhanced performance, security, and scalability. This technology enables businesses to utilize various transport services like MPLS, LTE, and broadband to connect users securely to applications, optimizing both cost and performance.
Key Features of SD-WAN
- Centralized Control and Management: SD-WAN solutions centralize network control, allowing for more efficient management and operation. This centralized approach simplifies the deployment and management of network services across multiple locations.
- Dynamic Path Selection and Application-Aware Routing: By intelligently routing traffic based on application needs and network conditions, SD-WAN improves network efficiency and performance. This feature also reduces latency and enhances the user experience by prioritizing critical applications.
- Enhanced Security: SD-WAN provides robust security features including end-to-end encryption across the entire network, advanced threat protection, and consistent policy enforcement across all locations. These features are crucial for protecting sensitive data and maintaining compliance with industry regulations.
Benefits of SD-WAN
- Cost Efficiency: By utilizing low-cost local Internet access, SD-WAN reduces the need for expensive leased lines. Organizations can lower overall WAN expenses while achieving high levels of reliability and network quality.
- Improved Network Agility: With SD-WAN, businesses can quickly adapt to changing network conditions and bandwidth demands. This agility supports cloud applications and services, ensuring optimal performance and accessibility.
- Simplified WAN Complexity: Traditional WAN architectures often require traffic to be routed through centralized data centers, which can lead to bottlenecks and reduced performance. SD-WAN eliminates these inefficiencies by enabling direct cloud access at the branch level, reducing latency and improving speed.
SD-WAN not only supports the current demand for high-bandwidth applications but also provides a scalable solution that can grow with the business. Its ability to manage multiple connection types and paths dynamically makes it an essential component of modern IT infrastructure.
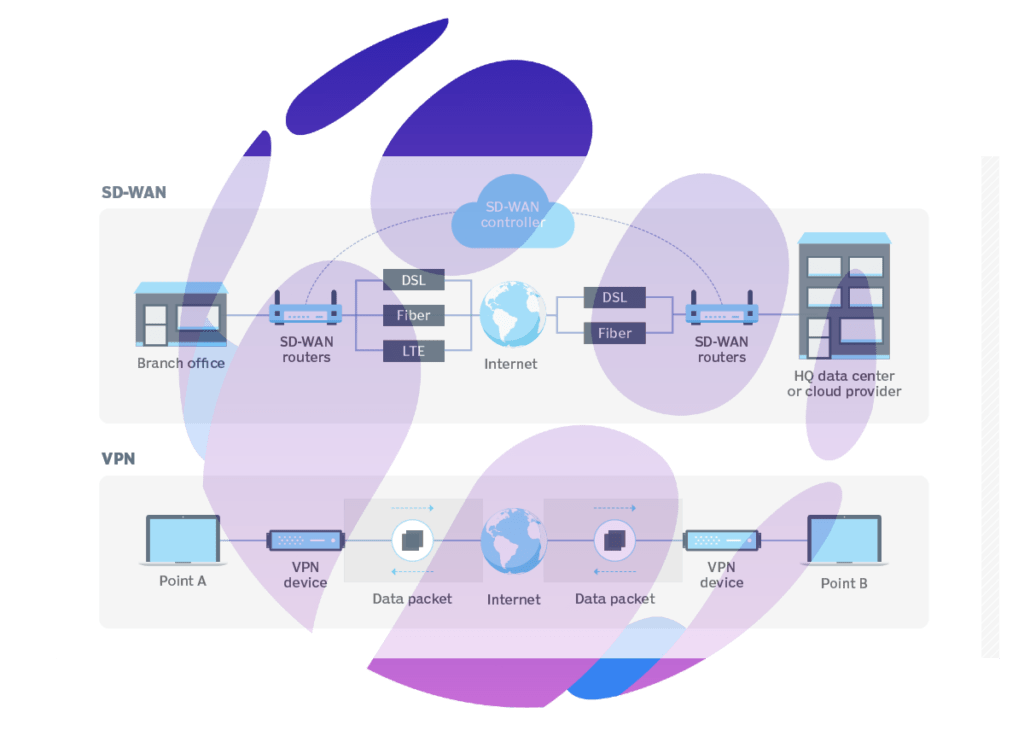
Comparative Analysis: Security
SD-WAN vs VPN: Security Architecture Differences
- Architectural Foundation:
- SD-WAN: Utilizes software-defined networking techniques to manage and optimize the WAN, providing dynamic path selection and centralized control.
- VPN: Relies primarily on a single, secure link for data transmission, using traditional routing methods.
- Security Implications:
- SD-WAN: Offers enhanced security features such as integrated firewalls, intrusion prevention systems, and the ability to segment the network, which can isolate and protect data flows.
- VPN: Focuses on encrypting data transmissions to secure data from unauthorized access, but lacks the dynamic and adaptive security measures provided by SD-WAN.
- Operational Efficiency:
- SD-WAN: By managing WANs using software-defined methods, SD-WAN can quickly adapt to changing security threats and network conditions, enhancing overall security posture.
- VPN: While effective in creating a secure tunnel for data, its dependence on a single link can be a limitation in scenarios where multiple dynamic paths would be more secure and efficient.
Comparative Analysis: Performance
SD-WAN Performance Features
- Dynamic Path Selection and Application-Aware Routing: SD-WAN technology enhances performance by utilizing dynamic path selection, which automatically chooses the best path for traffic based on current network conditions. This capability is complemented by application-aware routing that recognizes the type of application being used and prioritizes traffic accordingly to ensure optimal performance.
- Granular Traffic Control: With SD-WAN, administrators have granular controls allowing them to manage and monitor WAN traffic very precisely. This includes the ability to restrict traffic by type or user, enhancing both scalability and reliability. Real-time monitoring and management tools are integral to SD-WAN, providing insights that help in maintaining high performance across the network.
- Quality of Service (QoS) and Failover Capabilities: SD-WAN supports advanced QoS capabilities, prioritizing critical business applications and ensuring that performance levels meet user expectations. Additionally, SD-WAN’s failover features enhance network reliability by automatically rerouting traffic in case of service disruptions or outages, a significant performance advantage over traditional VPN solutions.
VPN Performance Limitations
- Dependence on Public Internet: VPNs primarily rely on the public internet for data transmission. This dependence can make VPNs vulnerable to common internet-related performance issues such as variable latency and bandwidth congestion, particularly when data has to travel long distances.
- Lack of Dynamic Routing: Unlike SD-WAN, traditional VPNs do not offer dynamic path selection or application-aware routing. This can lead to less efficient use of network resources, as all traffic is typically routed through a single secure tunnel regardless of the type of data or priority, potentially leading to bottlenecks and decreased performance.
By comparing these aspects, it’s evident that SD-WAN provides a more robust framework for managing network performance, especially in environments where traffic prioritization, flexibility, and real-time control are crucial.
Comparative Analysis: Cost-Effectiveness
When evaluating the cost-effectiveness of SD-WAN versus VPN, it’s important to consider both the initial costs and the long-term financial benefits that each technology can offer. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
Initial and Ongoing Costs
- VPN Solutions: VPNs are known for their straightforward and generally lower initial cost structure. They provide a basic yet effective solution for secure internet access and data encryption. This cost advantage makes VPNs particularly attractive to individuals and small businesses that require a simple, affordable way to secure their internet connections.
- SD-WAN Solutions: In contrast, SD-WAN solutions typically involve a higher initial investment. This is due to their more complex infrastructure and advanced features like dynamic path selection, application-aware routing, and centralized management. However, the higher upfront costs are often justified by the significant improvements in network management, efficiency, and scalability that SD-WAN provides.
Long-Term Financial Benefits
- Reduced Operational Costs with SD-WAN: Although the initial setup for SD-WAN is more costly, it can lead to considerable savings in operational expenses over time. By optimizing bandwidth usage and reducing the need for traditional WAN links, businesses can lower their monthly expenses related to network management and maintenance.
- ROI and Business Growth: SD-WAN not only helps in cutting down ongoing costs but also contributes to business growth by enhancing network performance and reliability. This can lead to improved productivity and customer satisfaction, which are crucial for long-term business success and can significantly offset the initial investment in SD-WAN technology.
In summary, while VPNs offer a cost-effective solution for basic network security needs, SD-WAN presents a more robust framework that, despite its higher initial cost, can provide substantial long-term savings and business advantages.
Wrapping Up the Differnces
Through the exploration of SD-WAN versus VPN technologies, it’s clear that each serves distinct needs with specific advantages for improving network performance and security. SD-WAN emerges as the go-to for businesses seeking advanced network management, scalability, and optimized performance, particularly for handling high-bandwidth applications and diverse network conditions. VPNs, meanwhile, continue to provide a solid foundation for ensuring data privacy and security, particularly appealing for individuals and smaller enterprises requiring a straightforward and cost-effective solution to protect their online activities.
Deciding on the right technology hinges not only on immediate networking needs but also on future scalability, performance requirements, and the strategic direction of business IT infrastructure. As such, finding the best IT company to set up your VPNs or SD-WAN becomes an essential step towards tailoring your network’s architecture to meet these demands effectively. By carefully weighing the comparative analyses and considering the long-term impacts on cost-effectiveness, businesses and individuals can make informed decisions that align with their goals, ensuring robust, secure, and efficient network operations tailored to their specific needs.
Find The Best IT Company near you to install your VPN or SD-Wan network!
FAQs
1. How do SD-WAN and site-to-site VPN differ?
SD-WAN is designed to optimize and manage connections across multiple locations such as data centers and branch offices. In contrast, a VPN primarily focuses on encrypting internet connections to provide secure remote access to a private network.
2. What are the limitations of using SD-WAN?
SD-WAN lacks on-site security features, meaning additional security measures must be implemented to protect the network from external threats. A single data breach could potentially compromise the entire network.
3. Why is a VPN generally less expensive than an SD-WAN?
Both VPN and SD-WAN are cost-effective as they utilize internet-based solutions. However, VPNs are typically cheaper than SD-WANs due to their simpler setup, making them ideal for businesses that require a straightforward WAN network for a limited number of sites.
4. What distinguishes SD-WAN from mesh VPN in terms of network management?
The key difference lies in the control structure. SD-WAN and SDN operate under a centralized control system, managing the entire network from a central point. Conversely, mesh VPNs operate on a decentralized model, where each node independently manages its connections with other nodes within the network.
